January 22, 2024
Dhaka – A NASA spacecraft orbiting the moon will send a laser beam that will now be reflected off a small mirror-based instrument aboard a lander on the moon’s surface, following India’s groundbreaking moon exploration mission last year. succeeded in.
NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), which has been orbiting the moon since June 2009, conducted a laser beam experiment on December 12 last year, and NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) announced the results on Friday. was announced.
This experiment will thus position ISRO’s lunar lander Vikram as a landmark in the south polar region of the moon.
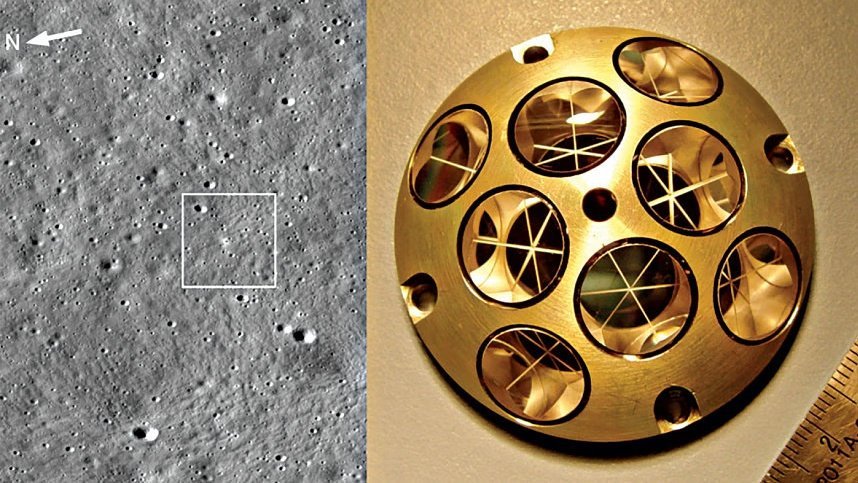
The beam sent from the LRO exited through a laser retroreflector array (LRA). A laser retroreflector array (LRA) is a 2-inch-wide dome-shaped device studded with eight finely polished mirrors designed to harness and reflect light coming from all directions. . said in a separate statement.
The distance between LRO and ISRO’s Chandrayaan-3 Vikram lander was 100 km, near the Manjinus crater in the lunar south pole region.
The success of the experiment will pave the way for the precise location of targets on the lunar surface. NASA’s Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA) was installed on board the Vikram lander in collaboration with ISRO.
The LRA has no electronics and requires no power or maintenance, allowing it to last for years.
“We have shown that we can locate retroreflectors on the surface from the moon’s orbit. The next step is to make it routine in future missions that want to use these retroreflectors. “The goal is to improve the technology to the next level,” the NASA statement quoted Xiaoli Sun, leader of the team that developed the LRA instrument, as saying.