of Populus Commonly known as poplar, cottonwood, and aspen, this genus consists of approximately 30 species of trees native to the Northern Hemisphere. Due to its diverse applications in landscape, agriculture, bioenergy and industry, Populus These species have been the focus of many tree breeding and genetic improvement programs. Modern biotechnology, including both genomics and genetic engineering (GE), is considered as a versatile tool to accelerate genetic engineering. Populus Domestication. moreover, P. trichocarpa The genome sequence was published in 2006, and advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) have since allowed researchers to explore the genetic basis of key features in the genome sequence. Populus. The CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing tool has been widely used to create a knockout of the hybrid poplar clone “717-1B4” (P. tremula × P. alba INRA 717-1B4). The development of alternative CRISPR-related tools, such as CRISRPa and base editing, has demonstrated great potential to improve plant fitness. However, the application of these new CRISPR tools Populus still very limited.
In May 2023, horticultural research Published a research paper titled “”.CRISPR/Cas9-based gene activation and base editing Populus ”.
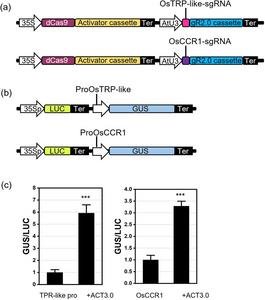
First, the researchers successfully constructed a high-throughput reporter gene-based CRISPRa evaluation system in protoplasts.they cloned the promoter Like OsTRP or OsCCR1 Gene generating reporter construct. By co-transfection of Like OsTRP When using the activation vector and its reporter vector in Arabidopsis protoplasts, the GUS/LUC ratio is 6-fold higher than that without the activation vector.Similar results were obtained for OsCCR1 gene. Next, we utilized this evaluation system to screen sgRNAs for gene activation. Populus protoplast. TPX2 and Rec RLK-G Essential for plant growth and defense. Cloning the 500 bp promoter region TPX2 and Rec RLK-G and inserted them into the reporter construct. Six and three sgRNAs were selected. TPX2 and Rec RLK-G Genes respectively. The activation efficiency of each sgRNA was evaluated by her GUS enzyme activity by co-transfecting the reporter construct and activation construct containing each sgRNA. Both sgRNA6 TPX2 and sgRNA6 Rec RLK-G selected for further stable transformation studies.
The identified sgRNAs were then used to establish stable transgenic poplars. In the hybrid poplar clone “717-1B4”, TPX2 Gene expression increased from 1.5 to 2.9 times. Similarly, in the clone “WV94”, Rec RLK-G Gene expression increased 2-fold and 7-fold in different events. These results demonstrate that the CRISPR-Act3.0 system can activate endogenous cells. TPX2 or Rec RLK-G Stable transgenic poplar genes. Additionally, this study cleaved the PLATZ protein associated with disease-related genes by introducing a premature termination codon using Cas9 nickase (nCas9)-based cytosine base editor (CBE) in poplar clone ‘717-1B4’. It was intended to. After identifying his two potential sites for introducing a stop codon, the researchers tested his two base editors (pHEE901(BE3) and A3A/Y130F-BE3) in poplar protoplasts. . Both editors effectively induced C to T mutations in the protoplast system. Furthermore, pHEE901(BE3) also showed the expected base editing in stable transgenic poplar.
In summary, this study introduces new applications of CRISPR tools, specifically CRISPRa and base editing, to enhance gene function in two ways. Populus seed. Remarkably, his dCas9-based CRISPRa system has been shown to effectively activate genes at different sites. Populus Genotype potential influence on phenotypic variation in future studies. This research establishes an important foundation for genetic improvement. Populusdemonstrates the vast potential of CRISPRa and base editing in woody species, and is expected to advance advances in tree breeding and other horticultural plants.
###
References
author
Tao Yao1, 2, †Guo Liangyuan1, 2, 3, †Highway Lou1,4,†Yang Liu1Jin Chang1,5Gerald A. Tuscan1, 2Wellington Muchello1, 2, *Jingyi Chen1, 2, * With Yang Xiaohan1, 2, *
†These authors contributed equally to this study
Affiliation
1. Department of Biosciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37831, USA.
2. Bioenergy Innovation Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37831, USA.
3. Chemical and Biological Process Development Group, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 902 Battelle Boulevard, Richland, WA 99352, USA.
4. Central Community College – Hastings School of Academic Education.Hastings; NE 68901, USA
5. National Key Laboratory of Subtropical Afforestation, School of Forestry and Biotechnology, Zhejiang Agriculture and Technology University.Hangzhou 311300, China
about Wellington Muchello & Jingyi Chen & Xiaohan Yang
Wellington Muchello: Dr. Wellington Muchello, a geneticist in the Division of Biological Sciences at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, conducts genome-wide association mapping studies, quantitative trait loci mapping, and functional validation of genes with a wide range of functions in eukaryotes. I am leading a discovery project using .
Jin-Gui Chen: Dr. Jin-Gui (Jay) Chen is a Distinguished Research and Development Staff Member in the Biosciences Division at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and a member of the Bredesen Center for Interdisciplinary Research and Graduate Education at the University of Tennessee. I’m also a teacher. Knoxville. He is a plant molecular biologist and geneticist who leads research tasks at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Center for Bioenergy Innovation (CBI), studying the control mechanisms underlying biomass productivity and properties.
Dr. Xiaohan Yang: Dr. Xiaohan Yang is a Distinguished Scientist in the Synthetic Biology Group in the Biological Sciences Division at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). His research focuses on plant genome editing, plant metabolic pathway engineering, plant-based biosensors, synthetic biology tool development, safe biosystem design, and bioenergy crops and plants to solve renewable energy and environmental challenges. and plant genomics with an emphasis on microbial interactions.
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! We are not responsible for the accuracy of news releases posted on EurekAlert! Use of Information by Contributing Institutions or via the EurekAlert System.